The vast majority of Chinese manganese ore belongs to the lean ore, beneficiation processing must be carried out. But because the majority of manganese ore is a fine-grained or micro-fine disseminated, and a considerable number of high-phosphorus ore, high iron ore and total (with) students useful metal, and therefore of great difficulty to the mineral processing. At present, the commonly used manganese ore beneficiation methods are mechanical selection (including washing, sieving, re-election, strong magnetic separation and flotation), as well as fire enrichment and chemical beneficiation.
1. Washing and sieving
Washing is the use of hydraulic washing or additional mechanical scrubbing to separate the ore from the mud. Commonly used equipment includes washing sieves, cylinder washing machines and tank washing machines. The washing operation is often accompanied by sieving, such as direct flushing on the vibrating screen or sifting the ore (net ore) obtained by the washing machine to the vibrating screen. Screening can be used as an independent operation to separate products of different sizes and grades for different purposes.
2. Re-election
At present, re-election is only used to select manganese ore with simple structure and coarse grain size, which is especially suitable for manganese oxide ore with high density. Common methods include heavy medium dressing, jigging and shaker dressing.
At present, the process of treating manganese oxide ore in China is generally to crush the ore to 6~0mm or 10~0mm, then group, coarse-grade jigging, and fine-level shaker selection. Most of the equipment is a Haz-type reciprocating jig and a 6-S shaker.
3. Strong magnetic selection
Manganese mineral is a weak magnetic mineral [specifical magnetization coefficient X=10×10-6~600×10-6cm3/g], and it can be used in a strong magnetic field magnetic separator with magnetic field strength Ho=800~1600kA/m (10000~20000oe). When recovered, it can generally increase the manganese grade by 4% to 10%.
Due to the simple operation, easy control and strong adaptability of magnetic separation, it can be used for various manganese ore sorting. In recent years, it has dominated manganese ore dressing. Various new types of coarse, medium and fine grain magnetic machines have been successfully developed. At present, the most common application of manganese ore in China is the medium-grain strong magnetic separator. The coarse-grained and fine-grained magnetic separators are gradually being applied. The micro-grain-strong magnetic separator is still in the experimental stage.
4. Heavy-magnetic separation
At present, the heavy-magnetic separation plants that have been newly built and reconstructed in China include Fujian Liancheng, Guangxi Longtou, Jingxi and Xialei. For example, Liancheng Manganese Mine Heavy-Magnetic Separation Plant mainly treats leaching manganese oxide ore, and uses AM-30 jig to treat 30~3mm washed ore, which can obtain high-quality manganese concentrate containing more than 40% manganese. After the removal of impurities, it can be used as a raw material for battery manganese powder. After jigging tailings and less than 3mm washing ore grinding to less than 1m, the selection of manganese ore concentrate should be increased by 24% to 25%, reaching 36% to 40%.
5. Strong magnetic - flotation
At present, only the Zunyi manganese ore is used in the strong magnetic-flotation process. The mine is a low-manganese, low-phosphorus, high-iron manganese ore mainly composed of manganese carbonate ore.
According to industrial tests, the grinding process uses rod mill-ball milling stage grinding, and the equipment scale is φ2100mm×3000mm wet grinding machine. The strong magnetic selection adopts the shp-2000 type strong magnetic machine, and the flotation machine mainly uses the CHF type inflatable flotation machine. After years of production test, the performance is good, it is very suitable for Zunyi manganese ore dressing application. The strong magnetic-flotation process has been successfully tested and applied in production, which indicates that the deep selection of manganese ore in China has taken a big step forward.
6. Fire law enrichment
The enrichment of manganese ore is a sorting method for the treatment of high-phosphorus and high-iron difficult-to-select manganese-poor ore. It is generally called manganese-rich slag method. The essence is a high-temperature sorting method for selectively separating manganese, phosphorus and iron by controlling the temperature of manganese, phosphorus and iron in different temperatures in a blast furnace or an electric furnace.
China has been using fire law for nearly 40 years. In 1959, Hunan Shaoyang Zijiang Iron Works was tested on a 9.4m3 small blast furnace and obtained preliminary results. Subsequently, in 1962, Shanghai Ferroalloy Plant and Shijingshan Iron and Steel Plant smelted manganese-rich slag in the blast furnace. In 1975, Hunan Agateshan manganese ore blast furnace not only produced manganese-rich slag, but also recovered lead , silver and pig iron (commonly known as semi-steel) at the bottom of the furnace, providing a basis for comprehensive utilization. After entering the 1980s, the production of manganese-rich slag has developed rapidly. The production of manganese-rich slag has been developed in Hunan, Hubei, Guangdong, Guangxi, Jiangxi, Liaoning, and Jilin.
The enrichment process of the fire method is simple, the production is stable, and the iron and phosphorus in the ore can be effectively separated to obtain manganese-rich, low-iron, low-phosphorus manganese-rich slag, and the manganese-rich slag generally contains Mn 35% to 45%. Mn/Fe 12-38, P/Mn<0.002, is a high-quality manganese-based alloy raw material, and it is also an artificial rich ore that is difficult to achieve the above three indexes at the same time. Therefore, the enrichment of fire method is a promising method for mineral processing in China for high-phosphorus high-iron and low-manganese refractory ore.
7. Chemical manganese selection
There are many chemical beneficiations of manganese. A lot of research work has been carried out in China, among which there are many experiments, and the development prospects are: dithionate method, manganese ore method and bacterial immersion method. It has not yet been put into industrial production.
â‘ Hardness:
Due to the scientific synthesis of high-molecular polyurethane elastomer materials using iron rubber, the higher the hardness, the higher the modulus, the smaller the elongation, and the better the wear resistance and heat resistance. Well, in the range of minus 35 degrees Celsius to 100 degrees Celsius, and at a pressure of 60 to 70 MPa, the maximum sealing performance can be guaranteed.
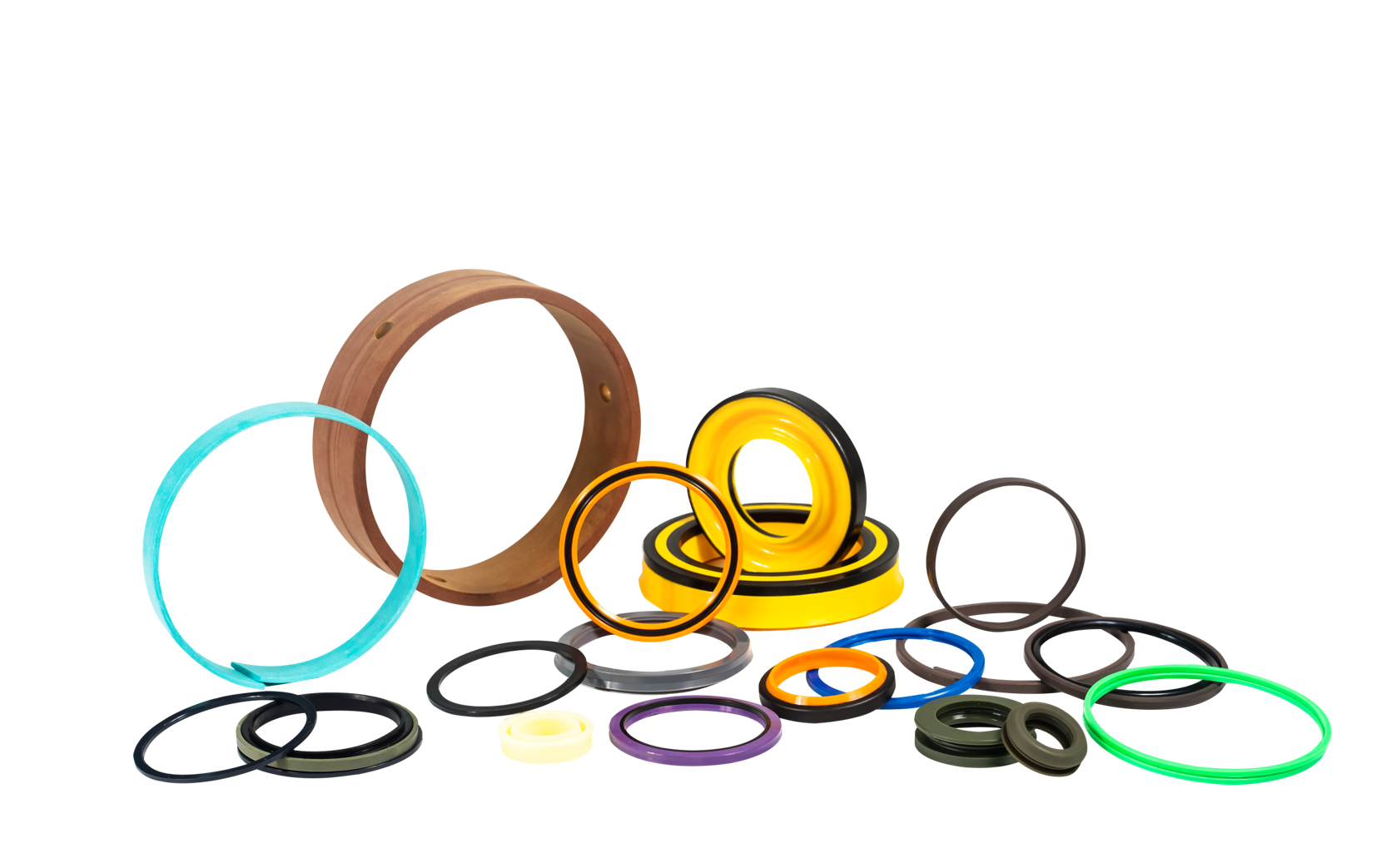

The use of viscoelastic seals made of nitrile rubber is the most complete protection against damage caused by back pressure. In the range of minus 55 degrees Celsius to 100 degrees Celsius, and under a pressure of 21MPa, due to the rubber The seal is often in a compressed state, so the compression performance of the rubber seal must be considered. It not only achieves enhanced anti-climbing performance and low friction resistance, but also has good performance in dealing with special low-temperature oil, and can also be used in combination with Anti-wear Ring double-purpose retaining ring BRL type.

Sealing products made of polytetrafluoroethylene and nitrile rubber/PTFErubber; or seals made of nylon resin and nitrile rubber, which can be used in a wide range of applications with large pressure changes and fast sliding speeds According to the working condition, the input hydraulic pressure cutout is designed on the end face of the polytetrafluoroethylene ring to prevent penetration leakage. The maximum working temperature environment is minus 40 degrees Celsius to 160 degrees Celsius; the maximum working pressure is 50MPa.
SPGW piston seal
Material:PTFE+rubber elastomer+reinforced modified nylon
Temperature:Nitrile rubber -40~100℃
Speed:=1.0m/s
Pressure:≤50mpa
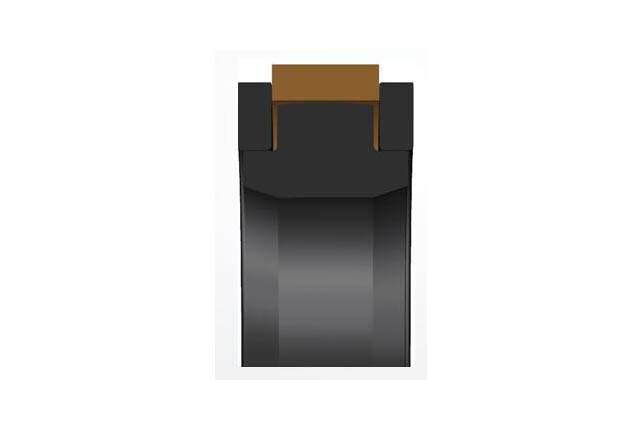
SPGO piston seal
Material:PTFE+rubber elastomer
Temperature:Nitrile rubber -40~110℃
Speed:=1.0m/s
Pressure:≤35mpa
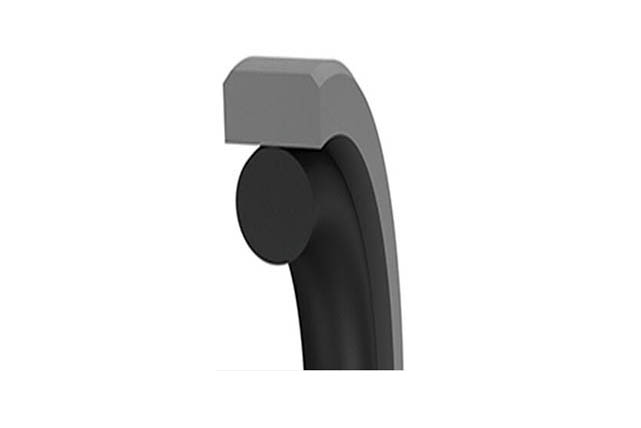

SRUV piston rod seal
Material:NBR+thermoplastic polyurethane
Temperature: -35`90℃
Speed:=0.5m/s
Pressure:≤40mpa
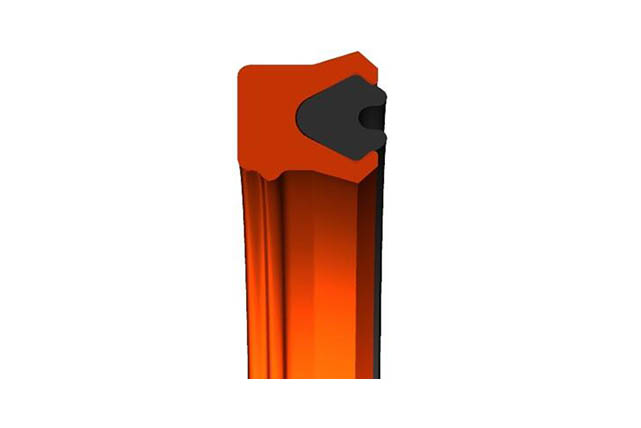

SRS piston rod seal
Material:PTFE+NBR
Temperature:-40~110℃
Speed:=1.0m/s
Pressure:≤40mpa
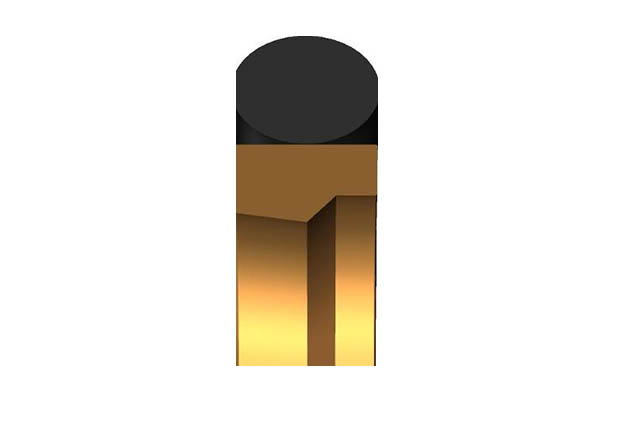

SRCB piston rod buffer seal
Material:Polyurethane+modified polyoxymethylene
Temperature: -35~110℃
Speed:=1.0m/s
Pressure:≤50mpa
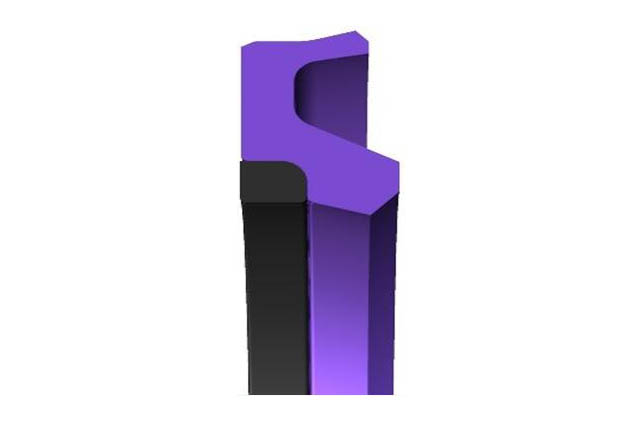

SRU piston rod seal
Material:Polyurethane
Temperature:-35~100℃
Speed:=1.0m/s
Pressure:≤40mpa
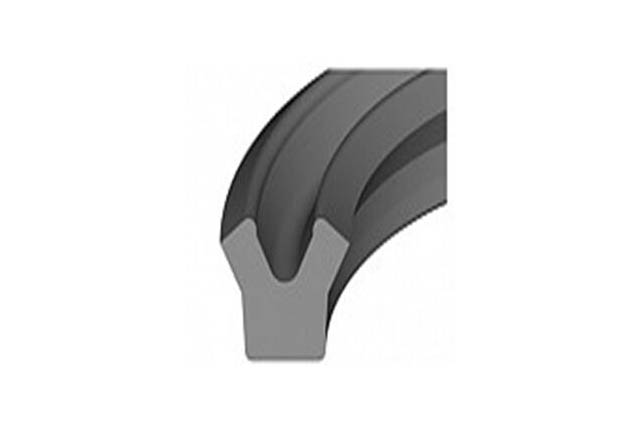

SRD iron case dust prevention
Material:Polyurethane+metal skeleton material
Temperature:-40~110℃
Speed:=1.0m/s
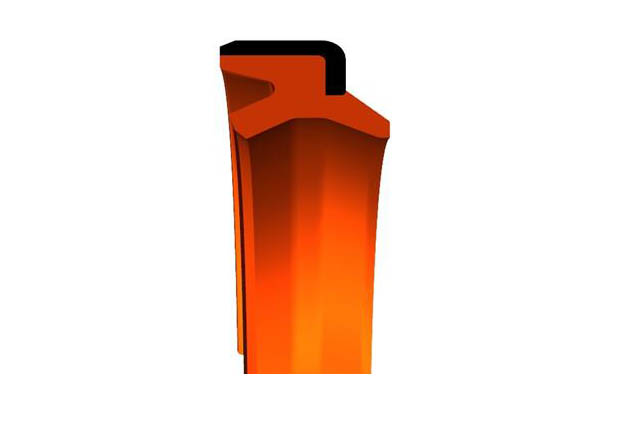

SRDI soft dustproof
Material:polyurethane
Temperature:-40~110℃
Speed:=1.0m/
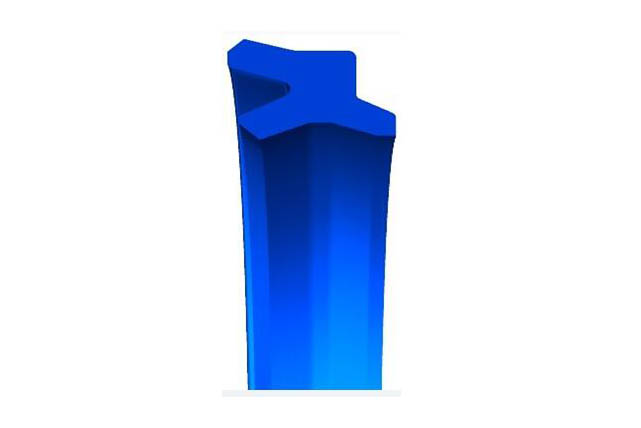

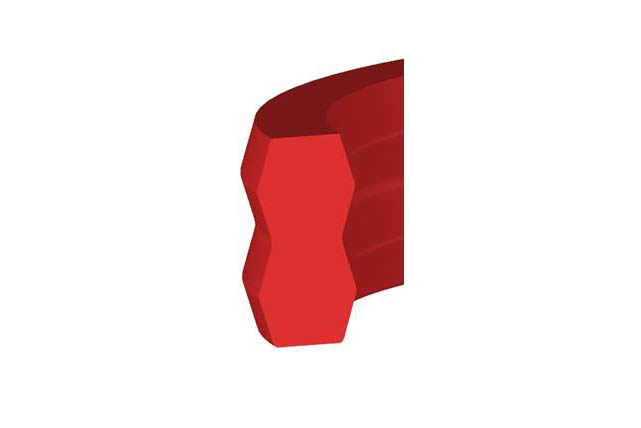
SDS Dumbbell Seal
Material:polyurethane
Temperature: -35~110℃
Speed:=0.5m/s
Pressure:≤50mpa
SPG piston combination seal
Temperature:
NBR+Polyurethane + Modified PolyoxymethyleneTemperature:-35`110℃
Speed:=0.3m/s
Pressure:≤70mpa
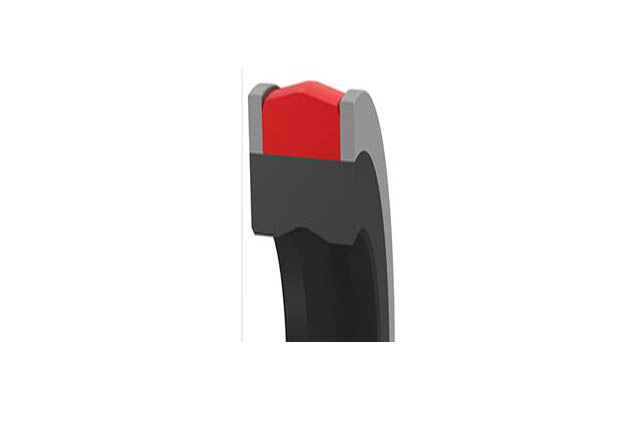

SRNL piston rod seal
Material
NBR+Polyurethane + Modified PolyoxymethyleneTemperature:-35`110℃
Speed:=0.3m/s
Pressure:≤70mpa
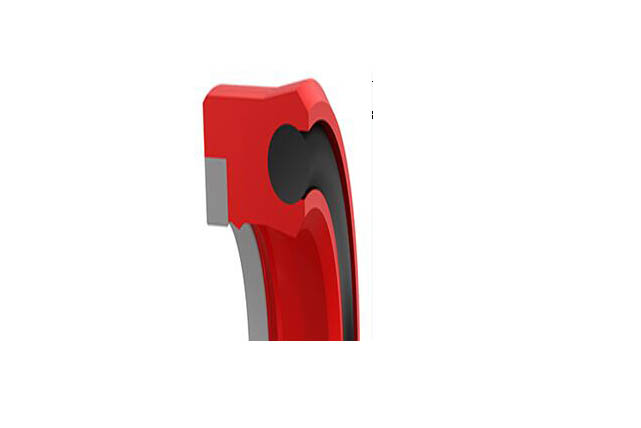

SRDF Piston Rod Seal
Material
Polyester rubberTemperature:-40`100℃
Speed:=1.0m/s
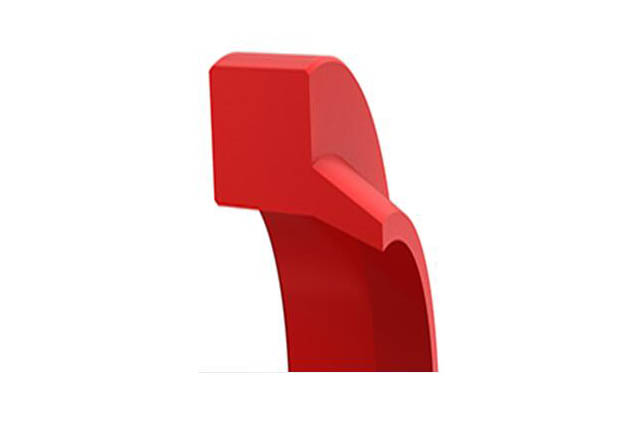

SDY Y-seal
Material:Polyurethane
Temperature:-35~110℃
Speed:=0.5m/s
Pressure:≤70mpa
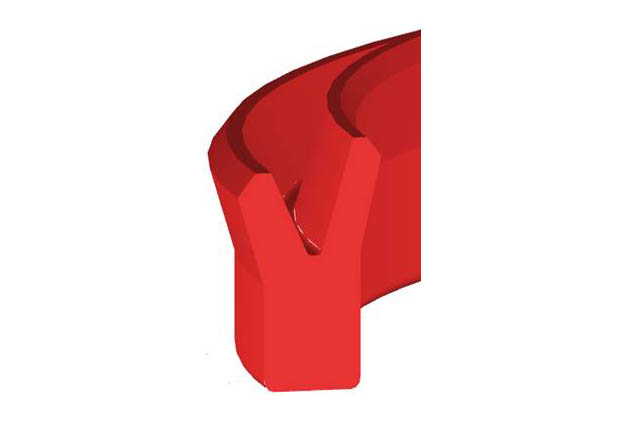

KZT anti fouling ring

SDS Steffel

Piston main oil seal
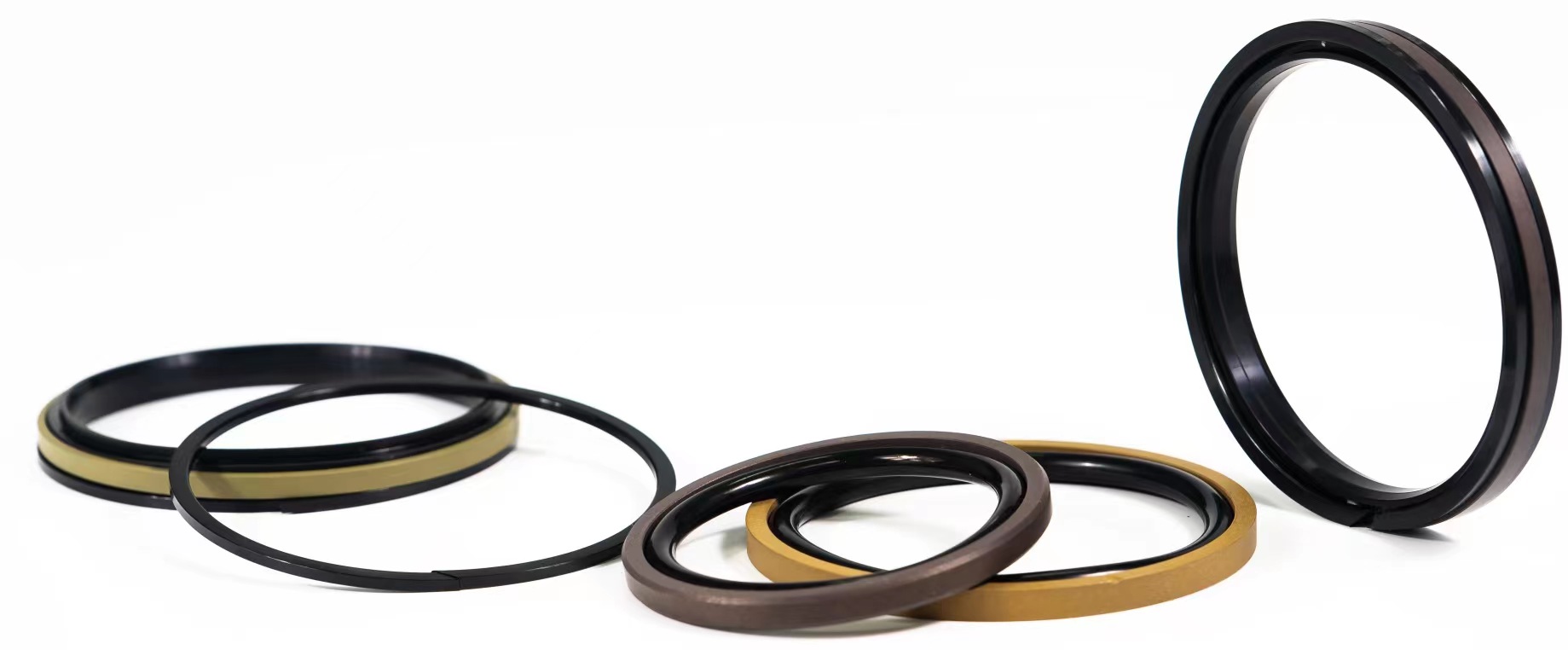

oil seals,hydraulic oil seal,track link oil seal,TCV oil seal,O-ring
Safe Seal Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.jsspreals.com
