 Wet gas flow meters are cumulative flow meters that record the total amount of gas flowing over a period of time. When the gas flows through the wet flow meter, the internal mechanical moving part divides the gas into a single known rotating volume under the action of the gas dynamics, and continuously fills and evacuates repeatedly, and records the cycle times through mechanical or electronic measurement technology. The cumulative flow of gas. Wet gas flow meters are often used in laboratory applications because of their own characteristics.
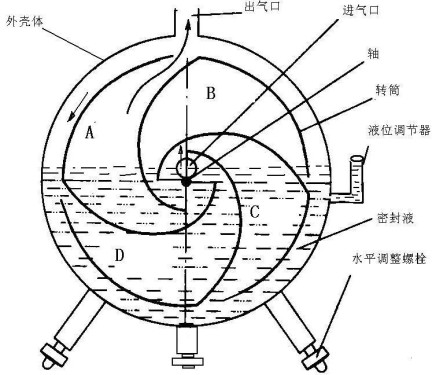
Wet gas flow meters are cumulative flow meters that record the total amount of gas flowing over a period of time. When the gas flows through the wet flow meter, the internal mechanical moving part divides the gas into a single known rotating volume under the action of the gas dynamics, and continuously fills and evacuates repeatedly, and records the cycle times through mechanical or electronic measurement technology. The cumulative flow of gas. Wet gas flow meters are often used in laboratory applications because of their own characteristics. First, the measurement principle and structure of the wet gas flow meter (a) structure principle Wet gas flowmeter was born in the United Kingdom in the early 19th century, after many technical improvements and improved principles into the current style (see Figure 1). It is a circular closed shell, followed by an intake pipe, the upper is an outlet pipe, inlet and outlet gas is sealed off with water or oil (the following example shows that water is the same). Above the level is installed and the connection hole for measuring temperature and pressure, the lower side has a drain valve, the side has a overflow valve port to control the liquid level, the bottom is 3 adjustable feet, can be adjusted to make the whole machine level, front It is a large disk pointer counter and 5-bit digital counter. Its internal structure is shown in Figure 2. The volume of the wet gas flow meter is a small measuring chamber divided into 4 (or 5) helical isolation chambers by the blades and drums. The drum is placed in the water (more than half of the water) in the shell and is supported by the horizontal axis. The rotation is flexible. In principle, when one metering chamber is inflated, at least one other metering chamber is vented. After a metering chamber is filled with gas, it must enter the exhaust position, so the starting point of the exhaust port of one metering chamber and the closing point of the inflation port must be synchronized on the fluid level line. In actual operation, the filling level line is lower than the exhaust level line, and the starting point of the exhaust port is a little behind the closing point of the filling port.
(B) level and liquid level adjustment Wet gas flowmeter measurement volume is mainly controlled by the level regulator, when installed in place and adjusted to the level (adjust the foot stud) state, the requirements of the wet gas flowmeter on the horizontal and The vertical spirit level bubble must be in the zero position. Unscrew the overflow valve and pour a certain amount of pure water from the upper water inlet. When the water is full (horizontal level inside and outside the shell is the same level), it will overflow from the overflow valve. After no overflow, closing the overflow valve can be detected. This work is very important. The position of the overflow valve has been adjusted at the factory inspection time. Generally, no change is required. If necessary, the water in the wet table can also be changed to white oil (No. 5). Due to the fact that only one central axis of the wet table rotates and the mechanical friction is small, the pressure loss of the wet table is very low (usually only a few hundred Pa) and the fluctuation is minimal. Its specifications are usually 0.5L, 1.5L, l0L, 20L, etc. The working pressure is generally not higher than 1500Pa, and the accuracy level in the measurement range can reach 0.5 class and 0.2 class.
Wet gas flowmeters are rarely used for on-site gas metering because of the high requirements of its use conditions, such as the level must be calibrated, must always check the liquid level, must be placed in a non-vibrating room, maintain a constant temperature, require the measured gas The temperament is clean, the working pressure can not be too high, it is more troublesome to use, but because its measurement accuracy can be very high (better than 0.2), the pressure loss is small, and it is affected by the density and dynamic viscosity of the gas to be measured. The small volumetric flowmeter has a wide range (100:1) ratio, so it is often used in laboratories or as a standard meter to check small gas flow meters such as diaphragm gas meters. It can also be tested in series at the same time. Multiple diaphragm gas meters, which are used as standard sheets for manufacturers of membrane meters, can increase production inspection efficiency. (However, at the same time, it is necessary to pay attention to the pressure compensation calculation when testing multiple membrane gas meters in series, otherwise the verification result will be wrong.)
The absolute error of the flow meter can be expressed as:
Where: V1 - flow meter indication (L);
V - The actual value (L) flowing through the flowmeter.
For the sake of comparison, the error of the flowmeter is usually indicated by the relative error. During the working process of the flowmeter, the "measurement chamber" appears between the measuring elements and between the measuring element and the housing one after another, and in the case of correct measurement. Next, gas is required to fill the entire "metering chamber." The volumetric flow through the flowmeter can be known only by knowing the volume of the "metering chamber" that is formed, the number of "metering chambers" that the measuring element operates once, and the number of times the measuring element is operated. If the volume of the "measurement chamber" is denoted as V' and the number of times constituting the "measurement chamber" is denoted as N, then the volumetric flow rate V measured by the N "measurement chambers" is different, and the measuring elements are formed during the operation. The N “measurement chambers†are converted through a series of gear transmission mechanisms and finally indicated in numerical form. If the values ​​displayed on the flow meter after the N “measurement chambers†are measured are denoted as V1, N The relationship between V1 can be expressed by the following formula:
Where: α - is a constant determined by the ratio of gears transmitting N "measurement chamber" values ​​and the scale value of one revolution, which is called transmission coefficient.
Substituting equation (4) into equation (3) yields equation (5) into equation (1). The error (6) of the flowmeter is the error characteristic of the flowmeter. Obviously, this error characteristic is completely The ratio of the “measurement chamber†volume V′ and the gear transmission coefficient α formed in the flowmeter is directly related to the working principle, the structure form, and the gear transmission method of the flowmeter, regardless of the shape and flow state of the fluid. This is one of the important features of the flowmeter. It is easy to see from equation (6) that when the transmission coefficient α is greater than the “volume chamber†volume V′, there is a positive deviation, indicating that the indicated value is greater than the actual flow rate, on the contrary, when α
However, this is only an ideal situation. Actually, such flowmeters will also be affected by various factors, such as the effect of air leakage, the effect of pressure loss, and the influence of fluid viscosity and density. So in actual conditions, the error curve of the flowmeter cannot be a straight line that is independent of the size of the flow.
Usage note: It is necessary to take into account whether the sealed liquid and the gas to be detected have a chemical or physical reaction. For example, ammonia is easily dissolved in water. Therefore, when ammonia is measured, water cannot be used as a sealed liquid. Or it should be noted that other chemical gases react with water to form additional substances.
The verification of wet gas flowmeters generally uses bell-type gas flow standard devices with higher accuracy levels, piston gas flow standard devices, or standard meter devices as standards. Check qmax and 0.2qmax flow points. During the test, the deviation between the actual flow rate at each flow point and the specified test flow shall not exceed 5%. At least 2 trials at each flow point.
Second, calibration and typical application LM series wet gas flow meter is one of the instruments commonly used in the laboratory. When measuring the total volume of gas, its accuracy is high, especially when it is small, its error is small. It can be used directly to measure the gas flow, and it can also be used as a standard instrument to verify other flow meters.
The effective volume of each gas chamber of the wet gas flowmeter is controlled by the surface of the water meter that is pre-injected into the flowmeter. Therefore, it must be checked whether the water surface reaches a predetermined position during use. When installing, the meter must be kept horizontal.
LM series wet gas flow meter is mainly divided into two types:
Normal type, brass material, generally used in the non-corrosive gas range.
Anti-corrosion type, stainless steel, can measure corrosive gases.
1. Wet gas flow meter selection model LML-1 (general), LML-2 (general), LMF-1 (corrosion), LMF-2 (corrosion)
2, the basic parameters of the drum flow per revolution (m3) 0.002 0.005
Rated flow (m3/h) 0.2 0.5
Maximum flow record (m3) 100 100
Excess flow (m3/h) 0.3 0.75
The minimum scale value (m3) 0.1×10-4 0.25×10-4
Normal pressure (Pa) 1000 1000
The rated flow accuracy is 1 or 0.5.
3, the use of methods (1) the instrument placed on the table, adjust the foot screws so that the level of blisters in the center, and in use to maintain long-term.
(2) Open the water level controller seal nut and pull out the internal wool rope.
(3) In the thermometer or pressure gauge jack, inject distilled water into the meter. When the distilled water flows out from the water level controller hole, stop injecting distilled water. When the extra distilled water flows from the water level controller hole along the rope, clean. (Approximately 5 to 10 minutes flow out when a drop is clean), the wool rope into the water level controller seal nut, and tighten the seal nut.
(4) Install the thermometer and pressure gauge. (Each cell 10Pa)
(5) Connect the gas line in the direction of the inlet and outlet gas, and keep it sealed.
4. Notes (1) During use, always pay attention to the water level in the meter. Otherwise, it will affect the measurement accuracy.
(2) In use, the temperature should be kept between 15~25°C, the temperature is the same as the room temperature, and the temperature difference should be ≤ 2°C.
(3) It is best to take readings after the meter pointer has run for several weeks.
(4) When the pressure of the gas to be measured exceeds the normal pressure value by 1 to 6 times (1 to 6) kPa, the instrument can still work. At this time, the pressure gauge should be removed, and the pressure gauge should be plugged with a holeless rubber stopper. hole.
(5) When the measured gas flow exceeds the rated flow to the excess flow range, the instrument can still work, but at this time the measurement accuracy will be reduced.
(6) When the meter is not in use for a long time, the distilled water in the meter should be kept clean. When discharging, use the drain valve first, and then turn the meter head downwards and then lower the air outlet pipe downwards. Repeat this several times to put the drum inside. The water is released.
(7) The instrument should not be placed in an over-cooled room to avoid internal ice formation.
(8) In normal use, at least once a year.
5, wet gas flowmeter calibration adjustment method:
(1) Preparation before verification: Add liquid, constant temperature, adjust the level of the whole machine, adjust the liquid level, and clean the blowpipe, and each step can not be less.
(2) Select the appropriate reading method: For the flow meter of the mechanical meter class, it is best to use the photoelectric conversion method to sample, automatically read, and achieve automatic detection, otherwise the repeatability of the flow meter cannot be realized.
(3) After over-level adjustment, it needs to be re-verified.
6. Notes for calibration:
(1) Imported wet gas flowmeters (without hands, or unstable liquids in the general trachea, to drain liquid)
(2) Domestic wet gas flowmeters (nuts with mechanical adjustment behind them, adjusted with needle-nose pliers, liquid level lines are placed in the liquid ports.)
(3) The pressure of the wet gas flowmeter should be observed and recorded. If the pressure difference is large, the cause must be found.
Conclusion: The wet gas flow meter requires proper use to play its role. When a user (such as a manufacturer) uses a wet gas flowmeter that has been calibrated in the measurement department, the liquid level line calibrated by the measurement department must be used in combination with the calibration certificate to determine if there is a meter factor to use the wet gas flowmeter correctly and scientifically. This unit correctly traces the source value and guarantees the correct delivery of the flow volume value.
Servo Spindle Motor,Cnc Lathe Spindle Motor,Cnc Servo Spindle Motor,Servo Spindle Motor Cnc
Ningbo junfa CNC Equipment Co. Ltd. , https://www.nbintimecnc.com
